110VAC/220VAC 120VA/240VACSplit-Phase Inverter Chargers for Reliable Power Solutions
H1: Understanding 110VAC/220VAC 120VA/240VACSplit-Phase Inverter Chargers for Reliable Power Solutions
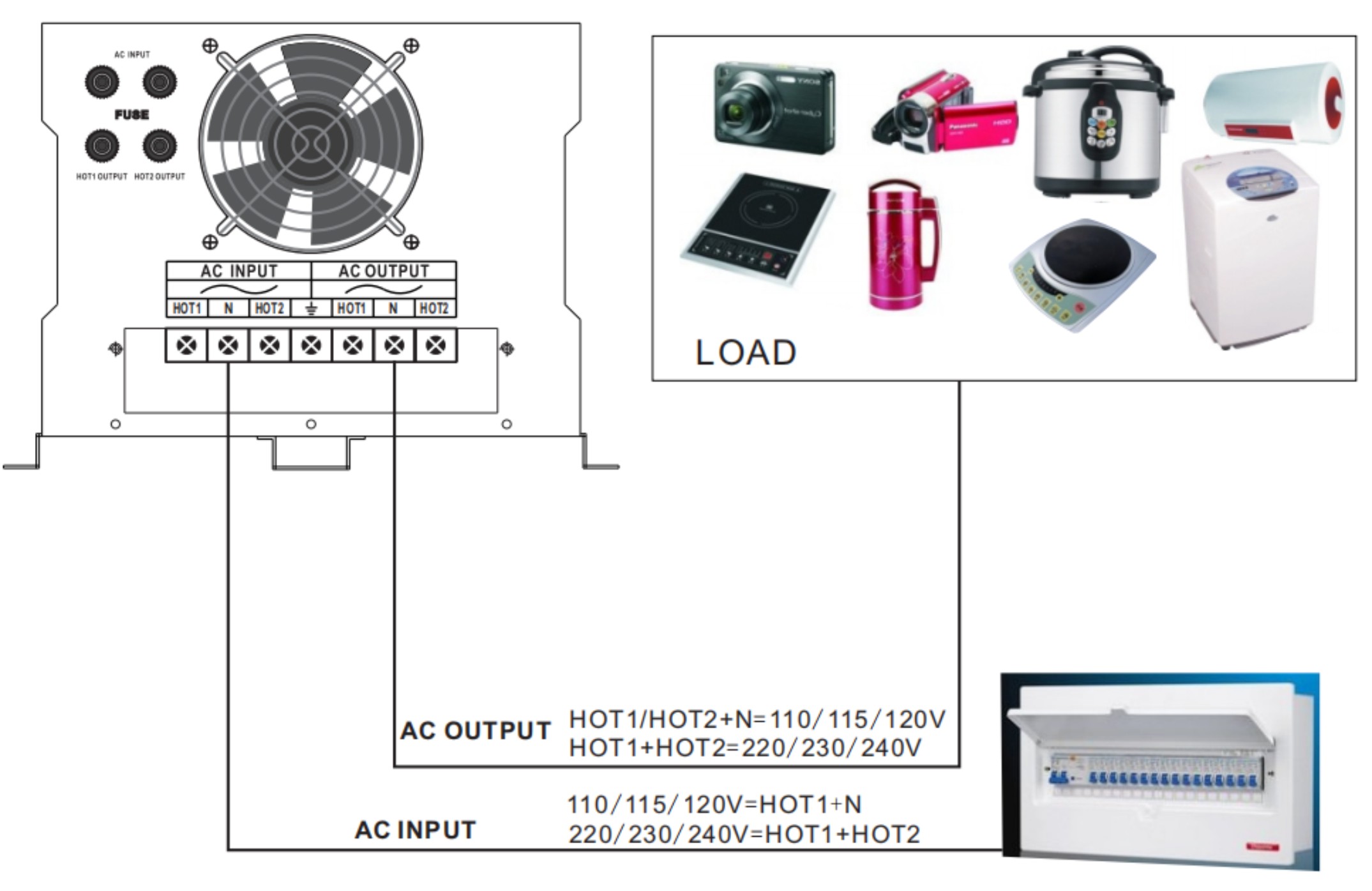
A split-phase inverter charger is a versatile device designed to convert DC power (from solar panels or batteries) into AC power with dual 120V outputs, which can be combined for 240V. It’s commonly used in countries like the U.S. and parts of South America Such as Colombia, Dominican Republic, Haiti, Venezuela, Ecuador, Honduras, and El Salvador to accommodate both 120V and 240V appliances.
H2: What is a Split-Phase Inverter Charger?
A split-phase inverter charger is designed to generate two 120V AC lines that are 180 degrees out of phase, creating a 220VAC or 240Vac connection when combined. This setup is ideal for powering a variety of appliances requiring different voltage levels and providing a balanced energy output across both phases.
.jpg)
H2: Differences Between Single-Phase and Split-Phase Inverter Chargers
1. Single-Phase Inverter: Produces only one 120V AC output, which limits it to lower-wattage appliances or regions that exclusively use 120V.The mains input has 1 live wire + 1 neutral wire
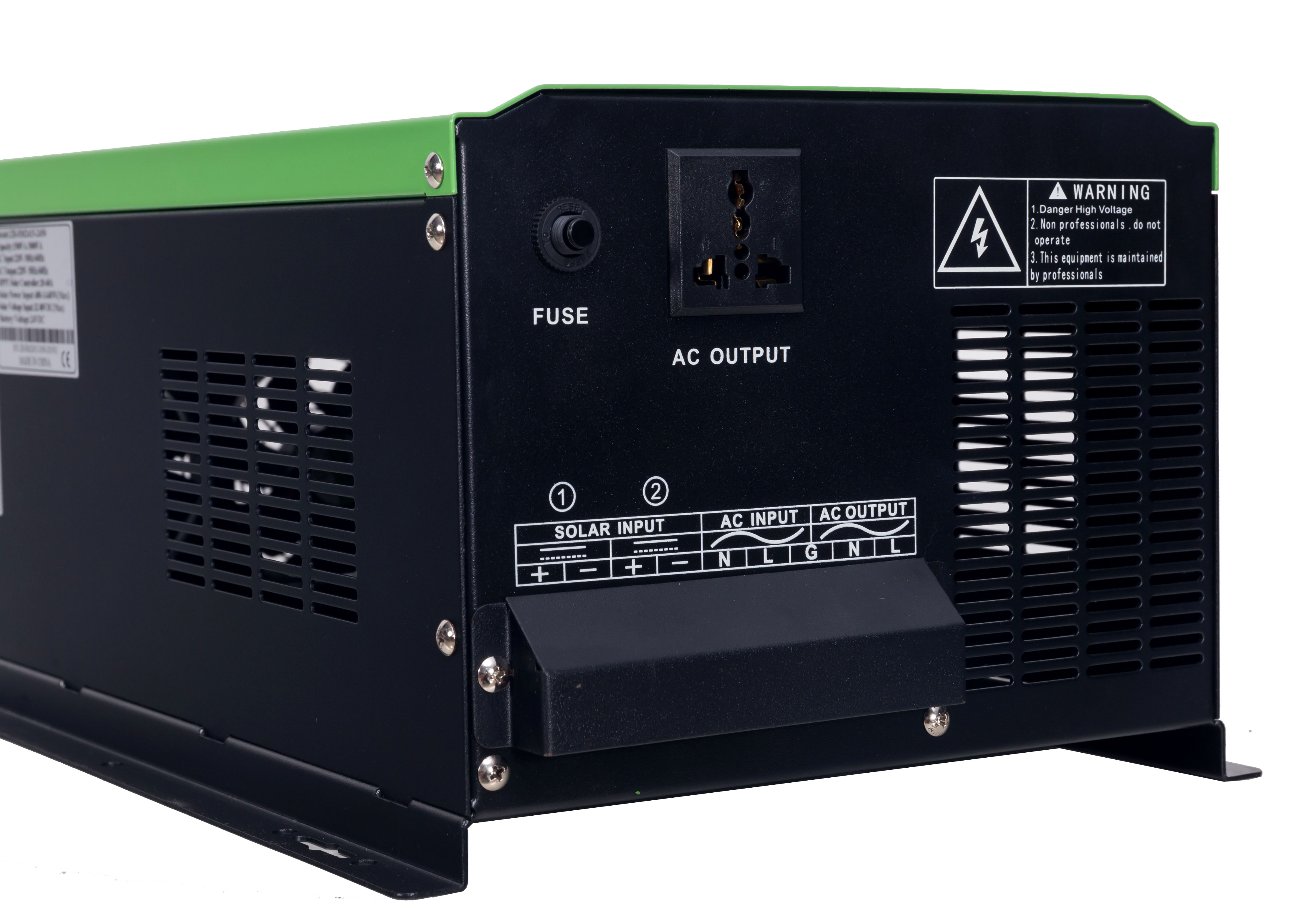

2. Split-Phase Inverter: Offers dual 120V outputs, which can also be combined to provide 240V for heavy-duty appliances, enabling greater versatility in regions with mixed voltage requirements. The mains input has 2 live wires + 1 neutral wire.
.jpg)
H2: How Does a Split-Phase Inverter Work?
A split-phase inverter uses a central transformer to create two 120V lines, each 180 degrees out of phase from the other. When these lines are combined, they produce 240V, allowing both light-duty and heavy-duty appliances to operate simultaneously.
H3: Appliances Compatible with Split-Phase Output
1. 110V-120V Output: Suitable for small household appliances like lighting, televisions, and kitchen gadgets.
2. 220V-240V Output: Supports high-wattage appliances such as ovens, air conditioners, and industrial equipment that need a stronger power source .
H2: What is Benefits of Using a Split-Phase Inverter
· Versatility: Enables compatibility with both 120V and 240V appliances.
· Balanced Load: Distributes power efficiently across phases, reducing load imbalances and potential strain.
· Adaptability: Perfect for areas with mixed power needs, providing an all-in-one solution .
H2: How to Distinguishing 120-Degree and 180-Degree Power in South America
IIn South America, power systems can vary, and distinguishing between 120-degree and 180-degree phase differences is important for ensuring proper inverter installation and compatibility.
· 120-Degree Phase: Typically used in regions with three-phase power setups.
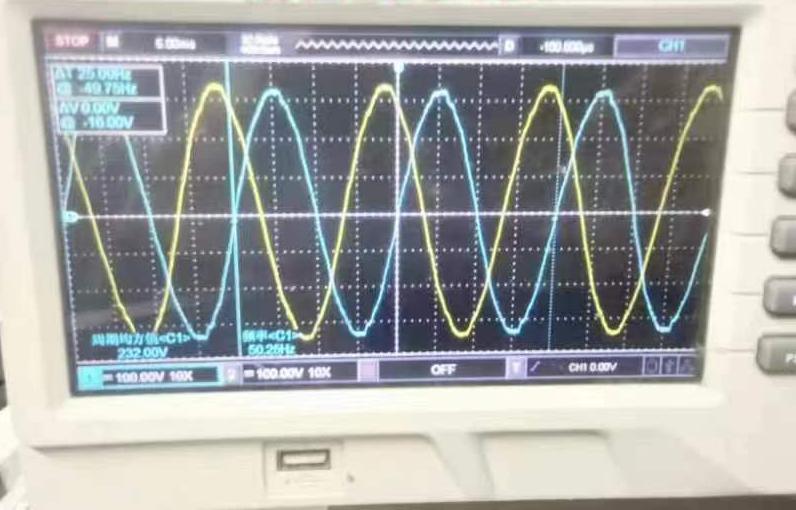
· 180-Degree Phase: Standard for split-phase power systems; compatible with split-phase inverters. Understanding these differences is essential to ensure compatibility with local power infrastructure.
1. 180-Degree Phase (Split-Phase):
· Typical in Residential Power: The U.S. and many South American countries use 180-degree phase difference for residential power, especially for split-phase systems.
· Voltage Characteristics: In this configuration, two 120V hot legs are 180 degrees apart. When combined, they produce 240V, allowing the use of both 120V and 240V appliances.
· Common Usage: Split-phase systems are most common for residential applications, powering everything from lighting and appliances to larger machines.
∵UAB=UA, UBC=UB, UCA=UC
∴UP=UL, line voltage=phase voltage
∴UAB=UAN*2, UAN=UAB/2
∴△φ=180°
When the inverter inputs the line voltage, it can be connected to the N line.
If :HOT1+ HOT2 Voltage 240VAC ≈(HOT1+N 120VAC)x2
AC Input Phase Voltage equal toΔφ=180°
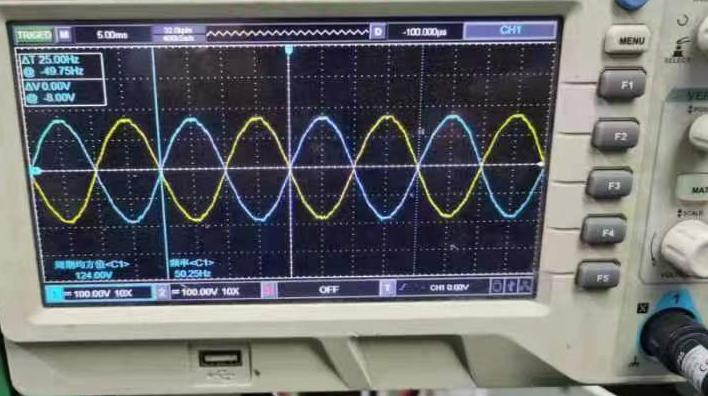
2. 120-Degree Phase (Three-Phase):
· Used in Industrial Applications: This phase configuration is commonly used in industrial and commercial power systems.
· Voltage Characteristics: The voltage between any two wires in a three-phase system is 120 degrees apart. This results in a more balanced load and is more efficient for transmitting electricity over long distances.
· Common Usage: Three-phase power is generally found in factories or areas requiring large-scale energy needs.

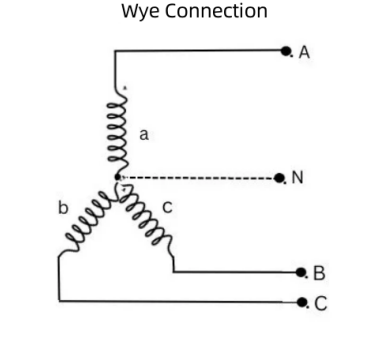
Star connection (Y connection):
∵UAB+UB-UA=0, UBC+UC-UB=0, UAC+UC-UA=0
∴UAB=UA-UB, UBC=UB-UC, UAC=UA-UC
∴UAB=1.732*UAN, UAN=UAB/1.732, line voltage=1.732*phase voltage∴△φ=120°
Please check the AC Input Voltage before connecting our split-phase inverter AC input!!!!!
If :HOT1+ HOT2 Voltage208V≈(HOT1+N 120VAC)x1.732
AC Input Phase Voltage equal toΔφ=120°
Selecting the Right Inverter for Diverse Power Needs
For optimal performance, it is essential to match the inverter type to local power configurations, especially in regions with non-standard phase requirements. Split-phase inverters can often accommodate these diverse needs due to their adaptable design. For more information on split-phase inverter parameters, please click herehttps://swnpower.com/products/67/3kw5kw6kw8kw10kw12kw-110vac-220vac-or-120v-240v-dual-output-split-phase-inverter

.jpg)